Free Classifieds at AUNetAds.com - View Item Content by ID 2286076

Item ID 2286076 in Category: Health & Beauty - Beauty
Cannot view this item. It could be pending, expired or deleted.
Below item is randomly selected from the same category and may have similar content.
20% OFF Entire Order on T3 Micro | |
Save 20% off entire order at T3 Micro when you use promo code LOUISAT3 at checkout. Shop premium hair tools and save today! 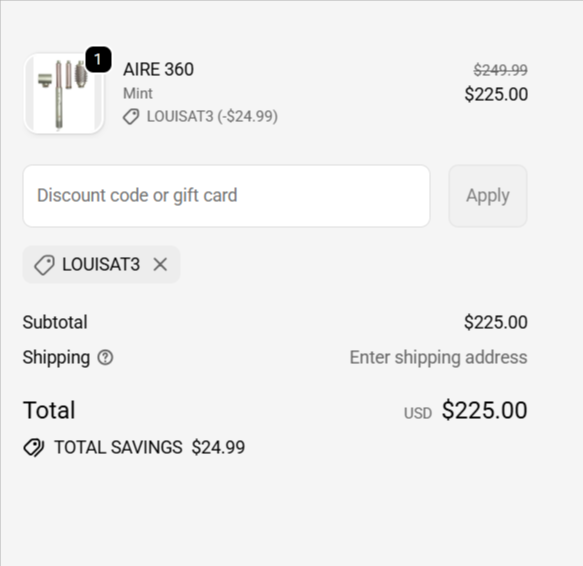 | |
| Related Link: Click here to visit item owner's website (0 hit) | |
| Target State: All States Target City : All Cities Last Update : 26 November 2025 10:00 PM Number of Views: 47 | Item Owner : Sumon Contact Email: (None) Contact Phone: (None) |
| Friendly reminder: Click here to read some tips. | |
© 2025 AUNetAds.com
USNetAds.com | GetJob.us | CANetAds.com | UKAdsList.com | INNetAds.com | CNNetAds.com | Hot-Web-Ads.com | USAOnlineClassifieds.com
2025-11-27 (0.333 sec)